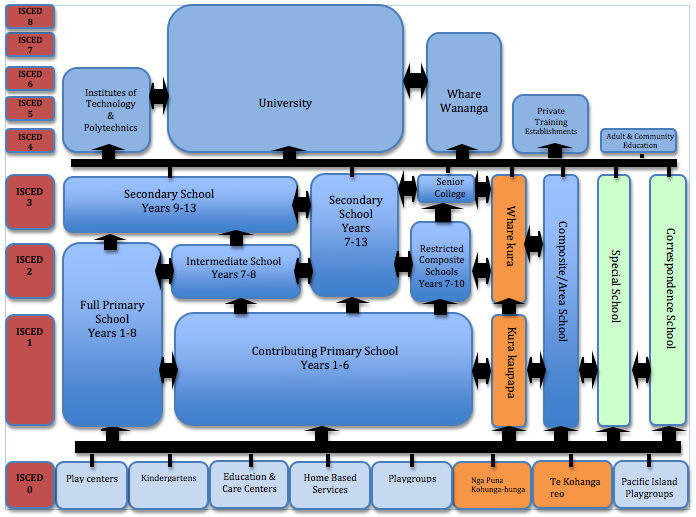
The structure of the education system is very flexible for students to navigate. Depending on geographical location, students are able to attend a variety of schools. Maori language immersion schools meet the needs of the Maori population. Many typical non-formal education practices are included in the formal education system including home schooling.
Early Education
In New Zealand Early Childhood Education (ECE) means education and care for children from babies to school entrant age. It is the first level of education. There is a wide range of ECE services including kindergartens, centre or home-based education and care, playgroups, play-centers and Köhanga Reo (centers teaching in full immersion in Maori language and culture).
Primary Education
Children may start school at age five and the majority do so, although schooling is not compulsory until the age of six. Primary education starts at Year 1 and continues until Year 8, with Years 7 and 8 mostly offered at either a primary or a separate intermediate school.
Secondary Education
Secondary education covers Years 9 to 13, during which students are generally aged 13 to 17. State secondary schools can be known as secondary schools, high schools or colleges. In secondary schools students experience a broad and balanced curriculum with some specialization possible especially in years 11 to 13.
Tertiary Education
Tertiary education in New Zealand is delivered by a variety of providers: universities, Institutes of Technology and Polytechnics, Private Training Establishments, Industry Training Organizations and Wänanga. These all deliver a variety of educational options, depending on the needs of the individual student.
(Source: World Data on Education, 7th Edition, 2011)